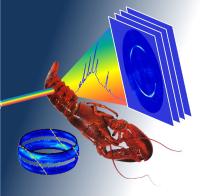
 Preferred crystal orientation (crystallographic texture) is a common phenomenon in many complex micro- and nanocrystalline materials of biological and synthetic origin. Conventionally, texture determination by XRD involves sample 2D diffraction images combined into 3D information by sample rotation. We have shown that the photon energies (“X-ray colours”) in a white X-ray beam can be exploited to gain direct 3D crystallographic information in texture measurements. The functionality of the method was demonstrated on carbon fibres and lobster cuticle.
Preferred crystal orientation (crystallographic texture) is a common phenomenon in many complex micro- and nanocrystalline materials of biological and synthetic origin. Conventionally, texture determination by XRD involves sample 2D diffraction images combined into 3D information by sample rotation. We have shown that the photon energies (“X-ray colours”) in a white X-ray beam can be exploited to gain direct 3D crystallographic information in texture measurements. The functionality of the method was demonstrated on carbon fibres and lobster cuticle.
Continue Reading
 A remarkably strong and anisotropic spin-phonon coupling was discovered for the ferromagnetic semiconductor europium monoxide through synchrotron experiments, inelastic X-ray scattering and nuclear inelastic scattering, and density functional theory. This discovery paves the way towards the design of spintronics devices with new functionalities.
A remarkably strong and anisotropic spin-phonon coupling was discovered for the ferromagnetic semiconductor europium monoxide through synchrotron experiments, inelastic X-ray scattering and nuclear inelastic scattering, and density functional theory. This discovery paves the way towards the design of spintronics devices with new functionalities.
Continue Reading
 On 28th June, the European Synchrotron welcomed Mr Dmitry LIVANOV, Minister of Education and Science of the Russian Federation, on the occasion of the 65th ESRF international Council meeting.
On 28th June, the European Synchrotron welcomed Mr Dmitry LIVANOV, Minister of Education and Science of the Russian Federation, on the occasion of the 65th ESRF international Council meeting.
Continue Reading
 Synthesis of new classes of compounds can lead to discoveries of novel physical phenomena as well as innovative applications. Fe4O5 is the first member of a very recently discovered family of iron oxides that can be synthesised only under high-pressure conditions. A multi-technique study of Fe4O5 reveals that it undergoes a unique charge-ordering transition below 150 K that involves competing dimeric and trimeric ordering within the chains of Fe ions. This electronic transition drives an intricate incommensurate distortion in its crystal structure.
Synthesis of new classes of compounds can lead to discoveries of novel physical phenomena as well as innovative applications. Fe4O5 is the first member of a very recently discovered family of iron oxides that can be synthesised only under high-pressure conditions. A multi-technique study of Fe4O5 reveals that it undergoes a unique charge-ordering transition below 150 K that involves competing dimeric and trimeric ordering within the chains of Fe ions. This electronic transition drives an intricate incommensurate distortion in its crystal structure.
Continue Reading
 Ведение поисковых экспериментов по созданию новых гетероструктур методом эпитаксии является интересным, но не всегда до конца предсказуемым процессом. В идеальном случае эпитаксиальная пленка вырастает на подложке в одной единственной заранее известной ориентации. Однако довольно часто при росте возникают неожиданные эпитаксиальные соотношения, вырастают новые малоизученные метастабильные фазы, появляются разно-ориентированные кристаллические решетки. Эффективным подходом, позволяющим разобраться в кристаллической структуре эпитаксиальных слоев, является применение трехмерного картографирования обратного пространства с помощью дифракционных методов. Помимо сведений о постоянных решетки, о пространственных группах и ориентациях, 3D картографирование позволяет также извлечь информацию о дефектной структуре эпитаксиальных слоев из распределения диффузной интенсивности вне узлов обратной решетки.
Ведение поисковых экспериментов по созданию новых гетероструктур методом эпитаксии является интересным, но не всегда до конца предсказуемым процессом. В идеальном случае эпитаксиальная пленка вырастает на подложке в одной единственной заранее известной ориентации. Однако довольно часто при росте возникают неожиданные эпитаксиальные соотношения, вырастают новые малоизученные метастабильные фазы, появляются разно-ориентированные кристаллические решетки. Эффективным подходом, позволяющим разобраться в кристаллической структуре эпитаксиальных слоев, является применение трехмерного картографирования обратного пространства с помощью дифракционных методов. Помимо сведений о постоянных решетки, о пространственных группах и ориентациях, 3D картографирование позволяет также извлечь информацию о дефектной структуре эпитаксиальных слоев из распределения диффузной интенсивности вне узлов обратной решетки.
Continue Reading
 Preferred crystal orientation (crystallographic texture) is a common phenomenon in many complex micro- and nanocrystalline materials of biological and synthetic origin. Conventionally, texture determination by XRD involves sample 2D diffraction images combined into 3D information by sample rotation. We have shown that the photon energies (“X-ray colours”) in a white X-ray beam can be exploited to gain direct 3D crystallographic information in texture measurements. The functionality of the method was demonstrated on carbon fibres and lobster cuticle.
Preferred crystal orientation (crystallographic texture) is a common phenomenon in many complex micro- and nanocrystalline materials of biological and synthetic origin. Conventionally, texture determination by XRD involves sample 2D diffraction images combined into 3D information by sample rotation. We have shown that the photon energies (“X-ray colours”) in a white X-ray beam can be exploited to gain direct 3D crystallographic information in texture measurements. The functionality of the method was demonstrated on carbon fibres and lobster cuticle.
 English
English  Русский
Русский  A remarkably strong and anisotropic spin-phonon coupling was discovered for the ferromagnetic semiconductor europium monoxide through synchrotron experiments, inelastic X-ray scattering and nuclear inelastic scattering, and density functional theory. This discovery paves the way towards the design of spintronics devices with new functionalities.
A remarkably strong and anisotropic spin-phonon coupling was discovered for the ferromagnetic semiconductor europium monoxide through synchrotron experiments, inelastic X-ray scattering and nuclear inelastic scattering, and density functional theory. This discovery paves the way towards the design of spintronics devices with new functionalities. On 28th June, the European Synchrotron welcomed Mr Dmitry LIVANOV, Minister of Education and Science of the Russian Federation, on the occasion of the 65th ESRF international Council meeting.
On 28th June, the European Synchrotron welcomed Mr Dmitry LIVANOV, Minister of Education and Science of the Russian Federation, on the occasion of the 65th ESRF international Council meeting. Synthesis of new classes of compounds can lead to discoveries of novel physical phenomena as well as innovative applications. Fe4O5 is the first member of a very recently discovered family of iron oxides that can be synthesised only under high-pressure conditions. A multi-technique study of Fe4O5 reveals that it undergoes a unique charge-ordering transition below 150 K that involves competing dimeric and trimeric ordering within the chains of Fe ions. This electronic transition drives an intricate incommensurate distortion in its crystal structure.
Synthesis of new classes of compounds can lead to discoveries of novel physical phenomena as well as innovative applications. Fe4O5 is the first member of a very recently discovered family of iron oxides that can be synthesised only under high-pressure conditions. A multi-technique study of Fe4O5 reveals that it undergoes a unique charge-ordering transition below 150 K that involves competing dimeric and trimeric ordering within the chains of Fe ions. This electronic transition drives an intricate incommensurate distortion in its crystal structure. Ведение поисковых экспериментов по созданию новых гетероструктур методом эпитаксии является интересным, но не всегда до конца предсказуемым процессом. В идеальном случае эпитаксиальная пленка вырастает на подложке в одной единственной заранее известной ориентации. Однако довольно часто при росте возникают неожиданные эпитаксиальные соотношения, вырастают новые малоизученные метастабильные фазы, появляются разно-ориентированные кристаллические решетки. Эффективным подходом, позволяющим разобраться в кристаллической структуре эпитаксиальных слоев, является применение трехмерного картографирования обратного пространства с помощью дифракционных методов. Помимо сведений о постоянных решетки, о пространственных группах и ориентациях, 3D картографирование позволяет также извлечь информацию о дефектной структуре эпитаксиальных слоев из распределения диффузной интенсивности вне узлов обратной решетки.
Ведение поисковых экспериментов по созданию новых гетероструктур методом эпитаксии является интересным, но не всегда до конца предсказуемым процессом. В идеальном случае эпитаксиальная пленка вырастает на подложке в одной единственной заранее известной ориентации. Однако довольно часто при росте возникают неожиданные эпитаксиальные соотношения, вырастают новые малоизученные метастабильные фазы, появляются разно-ориентированные кристаллические решетки. Эффективным подходом, позволяющим разобраться в кристаллической структуре эпитаксиальных слоев, является применение трехмерного картографирования обратного пространства с помощью дифракционных методов. Помимо сведений о постоянных решетки, о пространственных группах и ориентациях, 3D картографирование позволяет также извлечь информацию о дефектной структуре эпитаксиальных слоев из распределения диффузной интенсивности вне узлов обратной решетки.  Super elastic nickel-titanium (NiTi) alloys can tolerate large deformations due to a stress-induced martensitic transformation. When NiTi wire is stretched, a propagating macroscopic transformation front moves along the wire, separating transformed and untransformed regions, unlike other materials which deform homogenously. 3D-XRD stress tomography provided scientists with stress and strain tensors in austenite grains near this propagating front, and they could reconstruct a complete 3D picture of the front using digital image correlation and finite element modelling.
Super elastic nickel-titanium (NiTi) alloys can tolerate large deformations due to a stress-induced martensitic transformation. When NiTi wire is stretched, a propagating macroscopic transformation front moves along the wire, separating transformed and untransformed regions, unlike other materials which deform homogenously. 3D-XRD stress tomography provided scientists with stress and strain tensors in austenite grains near this propagating front, and they could reconstruct a complete 3D picture of the front using digital image correlation and finite element modelling.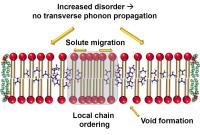
 The existence of single-atom magnets has been proven by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism. Monodisperse holmium atoms adsorbed on a nonmagnetic MgO thin film display magnetic hysteresis up to a temperature of 30 K and with magnetic relaxation time of the order of 1500 s. This stability is exceptional for such tiny structures. This study unveils key factors to improve the stability of atom-sized magnets in a solid state environment.
The existence of single-atom magnets has been proven by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism. Monodisperse holmium atoms adsorbed on a nonmagnetic MgO thin film display magnetic hysteresis up to a temperature of 30 K and with magnetic relaxation time of the order of 1500 s. This stability is exceptional for such tiny structures. This study unveils key factors to improve the stability of atom-sized magnets in a solid state environment.
